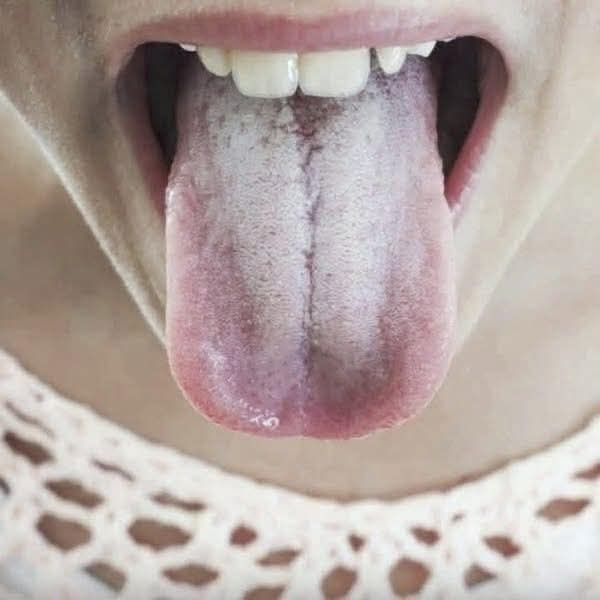
The appearance of a white coating on the tongue is a relatively common issue and can arise from a variety of causes. It is often benign, but in some cases, it can indicate an underlying health problem. If you’ve ever noticed your tongue looking white, it’s important to understand what might be happening and when you should seek medical advice.
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
One of the most common reasons for a white tongue is poor oral hygiene. When food particles, dead cells, and bacteria accumulate on the surface of the tongue, they can form a white coating. This can be exacerbated by not brushing the tongue while brushing your teeth or failing to clean your mouth properly.
Advertissement
Solution: Improve your oral hygiene routine. Brush your tongue gently with a toothbrush or use a tongue scraper to remove buildup. Regular brushing and flossing can also help prevent this.
2. Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body doesn’t have enough water to carry out normal functions. This can cause the tongue to appear white and dry. Dehydration is often a sign of insufficient fluid intake or excessive fluid loss due to conditions like fever or diarrhea.
Solution: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Dehydration can usually be resolved by increasing your fluid intake.
3. Oral Thrush (Candidiasis)
Oral thrush is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast in the mouth. It leads to the development of white, creamy patches on the tongue and other areas inside the mouth. Oral thrush is more common in individuals with weakened immune systems, those who use inhaled corticosteroids, or individuals who have diabetes.
Solution: Oral antifungal treatments, such as prescribed medications, are used to treat oral thrush. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions and maintain good oral hygiene.
4. Geographic Tongue
Geographic tongue is a benign condition in which areas of the tongue lose their normal pattern and develop smooth, red patches surrounded by a white border. These areas can change in shape and location over time, which is why it’s referred to as “geographic.”
Solution: Geographic tongue doesn’t require treatment unless it causes discomfort. If you experience pain, your doctor may suggest mouth rinses or topical treatments to alleviate symptoms.
5. Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia refers to white patches that form on the tongue or other areas inside the mouth. It is often linked to tobacco use, either smoking or chewing. While the condition is usually non-cancerous, it can sometimes be a precursor to oral cancer.
Solution: If you notice persistent white patches, especially if you smoke or use tobacco products, seek a medical opinion. In some cases, a biopsy may be needed to rule out precancerous changes.
6. Smoking and Alcohol Use
Both smoking and alcohol use can contribute to a white tongue. Smoking dries out the mouth and creates an environment conducive to bacterial and fungal growth. Alcohol, on the other hand, can lead to dehydration and affect the balance of oral bacteria.
Solution: Reducing or eliminating smoking and alcohol use can help prevent white tongue from occurring and promote better oral health.
7. Medical Conditions
Certain systemic conditions can contribute to the development of a white tongue. These include:
• Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to dry mouth and oral infections, which may result in a white tongue.
• Liver Disease: Liver problems can cause changes in the tongue’s appearance, including a white coating.
• Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus and Sjögren’s syndrome can affect the salivary glands, leading to dry mouth and a white tongue.
Solution: If you have any underlying medical conditions that may contribute to a white tongue, managing these conditions with the help of a healthcare provider can improve symptoms.
8. Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in your mouth, leading to an overgrowth of yeast (Candida) or other microorganisms, which may cause a white coating on the tongue.
Solution: If you develop a white tongue after taking antibiotics, the condition may resolve once the antibiotic course is completed. In some cases, your doctor may recommend antifungal treatments to address the overgrowth of yeast.
9. Dietary Factors
Certain dietary factors, such as a lack of essential vitamins (like vitamin B12) or a diet high in sugar, may contribute to a white tongue. High sugar intake can encourage the growth of harmful bacteria and yeast in the mouth.
Solution: Maintaining a balanced diet that includes essential vitamins and minerals can help improve the health of your tongue and oral cavity. Avoiding sugary foods and drinks can also reduce the risk of developing a white tongue.
10. Strep Throat or Other Infections
Infections like strep throat or a respiratory infection can lead to a white coating on the tongue, often accompanied by other symptoms such as sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes.
Solution: If a white tongue is accompanied by a sore throat, fever, or other symptoms of an infection, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment, which may include antibiotics for bacterial infections.
When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
While a white tongue is often not a cause for concern, there are certain situations where you should consult a doctor:
• If the white coating doesn’t go away after a few days.
• If it’s accompanied by pain or swelling.
• If you have difficulty swallowing or breathing.
• If you have a weakened immune system or underlying health conditions.
Your healthcare provider may perform a thorough examination, and in some cases, a biopsy may be needed to rule out more serious conditions, such as cancer or oral infections.
Conclusion
A white tongue can be a temporary or harmless condition, often resulting from poor oral hygiene, dehydration, or dietary factors. However, it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious health issue. Maintaining good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and addressing any underlying medical conditions can go a long way in preventing or treating a white tongue. If the condition persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, it’s important to seek professional medical advice.